Those knowledges about ELISA Plates
According to different classification standards, ELISA plates have different classifications.
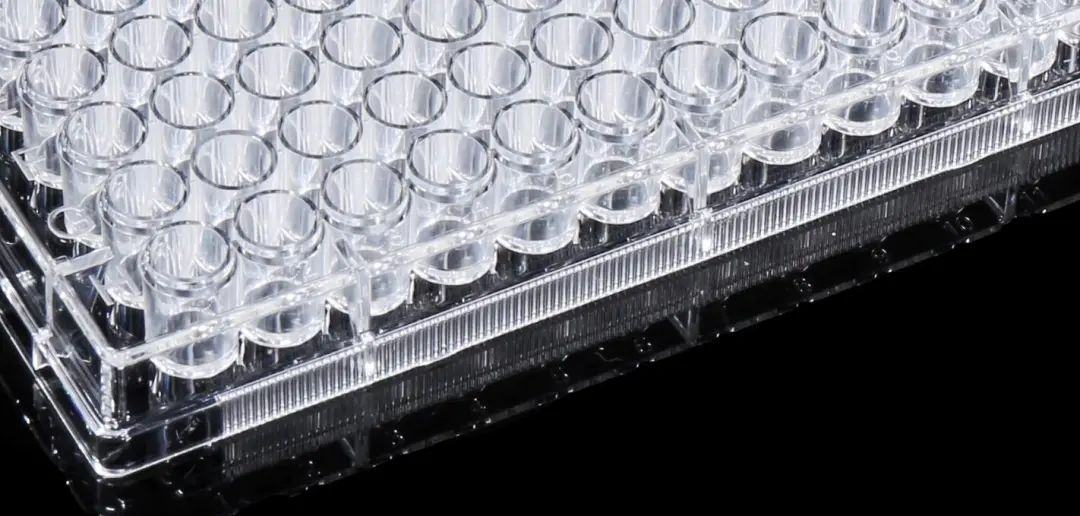
1. According to the number of wells, it can be divided into 96 wells and 48 wells, of which 96 wells are the most commonly used now, because the microplate reader is used with the microplate reader. Customers also want ELISA 96 Well Plate when they buy them in Beibei, and manufacturers basically make ELISA 96 Well Plate in order to adapt to the market.
2. According to the difference of the bottom, it is divided into flat bottom, U-shaped bottom and V-shaped bottom. The refractive index of the flat bottom is low, which is suitable for detection in the microplate reader: the microplate plate with a U-shaped bottom has a higher refractive index, which is convenient for operations such as sample addition, aspiration, and mixing. Observe the color changes to determine whether there is a corresponding immune response. The V-bottomed microtiter plate can accurately aspirate samples.
3. According to the different binding ability of the ELISA plate to protein and other molecules, it is divided into high binding force, medium binding force and amination.
1)high binding force
This ELISA plate, after the surface is treated, its protein binding ability is greatly enhanced, up to
300~400ng gG/cm2, the molecular weight of the main bound protein is >10kD. The use of this type of ELISA Microplate can improve the sensitivity, and can relatively reduce the concentration and dosage of the coated protein, but the disadvantage is that it is easy to produce non-specific reactions. After antigen or antibody coating, non-ionic detergents cannot effectively block unbound protein sites, so protein should be used as a blocking agent.
2)Medium binding force
This type of ELISA plate is passively bound to proteins through surface hydrophobic bonds, and is suitable as a solid-phase carrier for macromolecular proteins with a molecular weight of >20kD, and its protein binding capacity is 200~300ng?IgG/cm2. Due to the characteristics of this type of ELISA plate that only binds to macromolecules, it is suitable for use as a solid-phase carrier for unpurified antibodies or antigens, which can reduce potential non-specific cross-reactions. These plates can be blocked with inert proteins or non-ionic detergents.
3) Amination
This ELISA Microplate has an amino group with positive charge after surface modification, and its hydrophobic bond is replaced by a hydrophilic bond. This type of ELISA plate is suitable as a solid phase carrier for small molecular proteins. Use appropriate buffers and pH
value, its surface can bind negatively charged small molecules through ionic bonds. Due to the hydrophilic nature of its surface and its ability to be covalently bound by other cross-linking agents, it can be used to immobilize protein molecules dissolved in detergents such as Triton-100Tween™ 20. The disadvantage of this type of plate is that due to the reduced hydrophobicity, some protein molecules cannot be bound: in addition, its surface needs to be effectively blocked. Due to the hydrophilic and covalent surface properties, the blocking solution used must be able to interact with non-reactive amino groups and any functional groups in the chosen crosslinker.