How to use pipettes and tips
There is no doubt that pipettes are one of the most important tools for biological research. They come in a variety of designs and are used in countless areas of research. While many liquid handling guidelines emphasize the importance of pipette maintenance, pipette tips are equally important. Below, we share some of the top 10 tips for pipette use, pipetting operations to improve your pipetting technique.
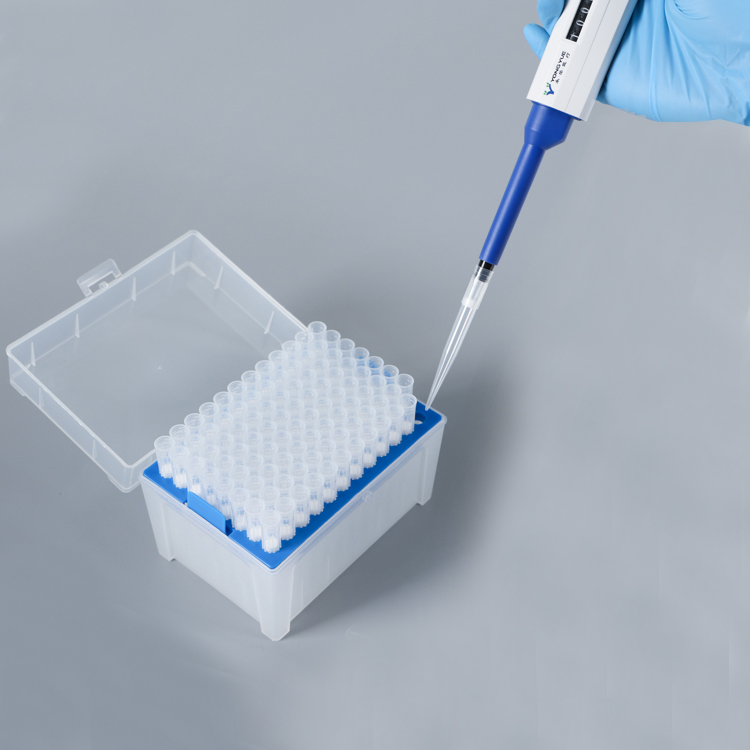

1. Choose the right single channel pipette and pipette tip: The match between the Manual Single Channel Pipette and the pipette tip is the key to pipetting accuracy. If the pipette tip and Single Channel Adjustable Pipettes do not match, or if a poor quality tip is used, the sealing performance between the tip and the pipette gun may be compromised. Good pipette tips ensure a proper seal, thus minimizing sample loss due to leakage.
2. Calibrate the pipette properly for the density of the liquid: If the density of the liquid differs significantly from that of water, recalibrate the pipette. If you are pipetting viscous liquids, ensure that you pipette at a slower rate and work in reverse pipette mode. When pipetting volatile liquids, you need to pipette quickly and use the reverse pipette mode.
3. Pre-wet the tip: To reduce liquid hang-up losses, pre-wet the tip at least 3 times. This wetting method helps establish temperature equilibrium and brings moisture into the dry space inside the tip. Skipping this step may affect the accuracy of the dispensed volume due to evaporation or liquid retention.
4. Proper aspiration: Immerse the tip below the liquid surface. When aspirating, the tip should not be immersed too deeply in the liquid, and the residence time in the liquid should be about 1S, because immersing too shallowly or too deeply may result in inaccurate aspiration.
Pipette holder
5. Pause after each aspiration: A slow, even, abrupt release helps reduce the occurrence of errors. This is especially important when working with viscous liquids. Whenever possible, try to sustain a pause of one to two seconds after each aspiration to keep the liquid level stable in the tip.
6. The use of pipettes also requires attention to the tilt angle of the pipette: Also, pay attention to the tilt angle of the pipette during operation, try to ensure vertical aspiration and maintain a tilt angle range of no more than 20°. When aspirating, the pipette tip should not touch the wall of the container as much as possible, especially when handling microscopic samples.
7. Adjust to the proper gear: Use a consistent and stable speed and pressure when handling pipettes and samples. The Rainin pipettes are designed with two gears, one and two, to ensure accurate pipetting. You can select the appropriate gear for pipetting according to your experimental and usage habits.
8. Pay attention to temperature: If your experiment allows, make sure the pipette, tips and liquid are at room temperature. Temperature changes and air pressure changes can also cause air in the pipette tip to contract or expand, which may affect the accuracy of dispensing liquids. In addition, try to avoid over-handling the pipette and tips, as your body temperature may also affect the amount of liquid dispensed. When the pipetting operation is complete, place it in the pipette holder and do not leave it lying around on the lab bench.
9. Do routine maintenance and care: Instrument calibration as well as routine maintenance is also an effective means to extend the life of the pipette gun, so it is recommended that the pipette be cleaned and maintained regularly on a weekly or monthly basis and calibrated regularly to improve its accuracy.
10. Develop good pipette operating habits: The development of pipetting operating habits is often overlooked, such habits include not only the correct and skilled skills in using the pipette gun but also the posture of the pipetting experiment, if the incorrect posture of the pipette, repeated operation for a long time may put your muscles in a state of tension or even muscle strain, the solution to this problem can be achieved by choosing a pipette that conforms to the mechanics of ergonomics. This problem can be solved by using ergonomic pipettes, developing good pipetting habits, etc.
——